Maven依赖引入
1.单项目
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId></groupId>
<artifactId></artifactId>
<version></version>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>- groupId:组织或公司名称,通常是反向域名。例如,
org.springframework.boot - artifactId:项目名称或模块名称。例如,
spring-boot-starter-web - version:依赖项的版本号。例如,
2.5.4
2. 多模块项目
<dependencyManagement> 标签用于集中管理依赖版本。它允许你在父 POM 文件中定义依赖的版本,然后在子模块中引用这些依赖,而无需在每个子模块中重复指定版本。
父POM文件
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>parent-project</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<modules>
<module>module-a</module>
<module>module-b</module>
</modules>
</project>子POM文件
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>parent-project</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>module-a</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>在 pom.xml 文件中,可以添加 <properties> 标签来定义依赖的版本号:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>my-app</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<spring.boot.version>2.5.4</spring.boot.version>
<mysql.connector.version>8.0.26</mysql.connector.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.boot.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
<version>${spring.boot.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql.connector.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>使用 <properties> 标签来集中管理依赖的版本号。这种方法可以使版本号在整个项目中保持一致,并且更容易维护。
在子模块没有引入相应依赖的时候,父POM不会将依赖注入到项目中。(不用担心父POM中的error)
Knife4j配置
knife4j官方文档:https://doc.xiaominfo.com/docs/quick-start
1. 依赖引入
<!--knife4j文档-->
<!--官方文档:https://doc.xiaominfo.com/docs/quick-start -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.xiaoymin</groupId>
<artifactId>knife4j-openapi3-jakarta-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${knife4j.version}</version>
</dependency>2. 配置类
2.1 在不使用 @EnableSwagger2WebMvc 的情况下配置 Knife4j
@Configuration
public class Knife4jConfiguration {
@Bean
public OpenAPI customOpenAPI() {
return new OpenAPI()
.info(new Info()
.title("API 文档")
.version("1.0")
.description("接口描述")
.termsOfService("http://doc.xiaominfo.com")
.license(new License()
.name("Apache 2.0")
.url("http://doc.xiaominfo.com")));
}
// 将接口分组
@Bean
public GroupedOpenApi systemAPI() {
return GroupedOpenApi.builder()
.group("系统信息管理")
.pathsToMatch(
"/admin/system/**"
)
.build();
}
}2.2 使用 @EnableSwagger2WebMvc 的情况下配置 Knife4j
To Do…
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2WebMvc
public class Knife4jConfiguration {
@Bean(value = "defaultApi2")
public Docket defaultApi2() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.groupName("2.X版本")
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.github.xiaoymin.knife4j.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("API 文档")
.description("# swagger-bootstrap-ui-demo RESTful APIs")
.termsOfServiceUrl("http://www.xx.com/")
.contact("xx@qq.com")
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}3. 创建控制器
@Tag(name = "首页模块")
@RestController
public class IndexController {
@Operation(summary = "向客人问好")
@GetMapping("/sayHi")
public ResponseEntity<String> sayHi(@RequestParam(value = "name") String name) {
return ResponseEntity.ok("Hi: " + name);
}
}4. 启动项目
启动 Spring Boot 项目,并在浏览器中访问 http://localhost:8080/doc.html 查看生成的 API 文档。
5. 相关配置
- SpringDoc OpenAPI 的一个配置选项,用于控制参数对象的展平方式。具体来说,这个配置项决定了在生成 OpenAPI 文档时,是否将参数对象展平为单个参数,而不是嵌套对象。
springdoc:
default-flat-param-object: trueMyBatis
1. <resultMap>元素
<resultMap> 元素用于定义结果映射。它包含多个 <result>、<id> 和 <association> 等子元素,用于指定如何将查询结果映射到 Java 对象的属性上。
2. 示例代码
User.java
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String email;
// Getters and Setters
}UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.mapper.UserMapper">
<!-- 定义 resultMap -->
<resultMap id="userResultMap" type="com.example.model.User">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="name" column="name" />
<result property="email" column="email" />
</resultMap>
<!-- 使用 resultMap 的查询语句 -->
<select id="selectAllUsers" resultMap="userResultMap">
SELECT * FROM users
</select>
</mapper>可以使用
<resultMap id="?" type="?" autoMapping="true">会将resultMapping中的字段按照名称相同的方式映射到返回类型的对应属性上,在映射时会自动忽略大小写。Mybatis的自动映射策略默认是开启的,而且默认是只对非嵌套的resultMap进行自动映射。
<resultMap>:定义结果映射,id是结果映射的唯一标识符,type是映射的 Java 对象类型。<id>:指定主键属性的映射,property是 Java 对象的属性名,column是数据库表的列名。<result>:指定普通属性的映射,property是 Java 对象的属性名,column是数据库表的列名。<select>:使用<resultMap>的查询语句,resultMap属性指定使用的结果映射。
3. 复杂映射
如果查询结果包含嵌套对象,可以使用 <association> 和 <collection> 元素进行复杂映射。
Order.java
public class Order {
private int id;
private User user;
private String orderNumber;
// Getters and Setters
}OrderMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.example.mapper.OrderMapper">
<!-- 定义嵌套 resultMap -->
<resultMap id="orderResultMap" type="com.example.model.Order">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="orderNumber" column="order_number" />
<association property="user" javaType="com.example.model.User" resultMap="com.example.mapper.UserMapper.userResultMap" />
</resultMap>
<!-- 使用嵌套 resultMap 的查询语句 -->
<select id="selectAllOrders" resultMap="orderResultMap">
SELECT o.id, o.order_number, u.id AS user_id, u.name, u.email
FROM orders o
JOIN users u ON o.user_id = u.id
</select>
</mapper><association>:用于映射嵌套对象,property是 Java 对象的属性名,javaType是嵌套对象的类型,resultMap是嵌套对象的结果映射。<collection>: MyBatis 中用于定义一对多关系映射的元素,它允许将查询结果中的多个记录映射到一个 Java 对象的集合属性上。例如Java中List类型的对象。
知识点
xml文件的
<和>的转义原符号 转义符号 <<>>Mybatis-Plus分页插件注意事项
使用Mybatis-Plus的分页插件进行分页查询时,如果结果需要使用
<collection>进行映射,只能使用 嵌套查询(Nested Select for Collection),而不能使用 嵌套结果映射(Nested Results for Collection)。嵌套查询和嵌套结果映射是Collection映射的两种方式,下面通过一个案例进行介绍
例如有
room_info和graph_info两张表,其关系为一对多,如下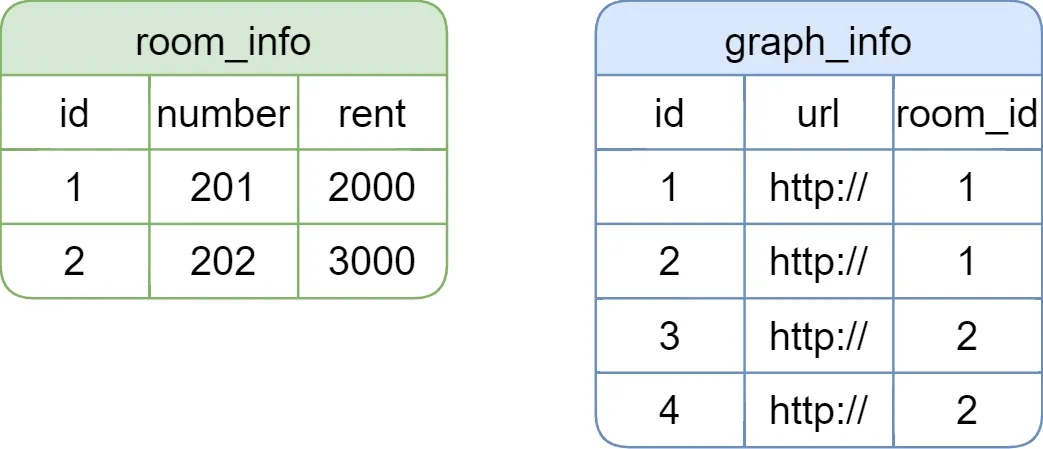
现需要查询房间列表及其图片信息,期望返回的结果如下
[ { "id": 1, "number": 201, "rent": 2000, "graphList": [ { "id": 1, "url": "http://", "roomId": 1 }, { "id": 2, "url": "http://", "roomId": 1 } ] }, { "id": 2, "number": 202, "rent": 3000, "graphList": [ { "id": 3, "url": "http://", "roomId": 2 }, { "id": 4, "url": "http://", "roomId": 2 } ] } ]为得到上述结果,可使用以下两种方式
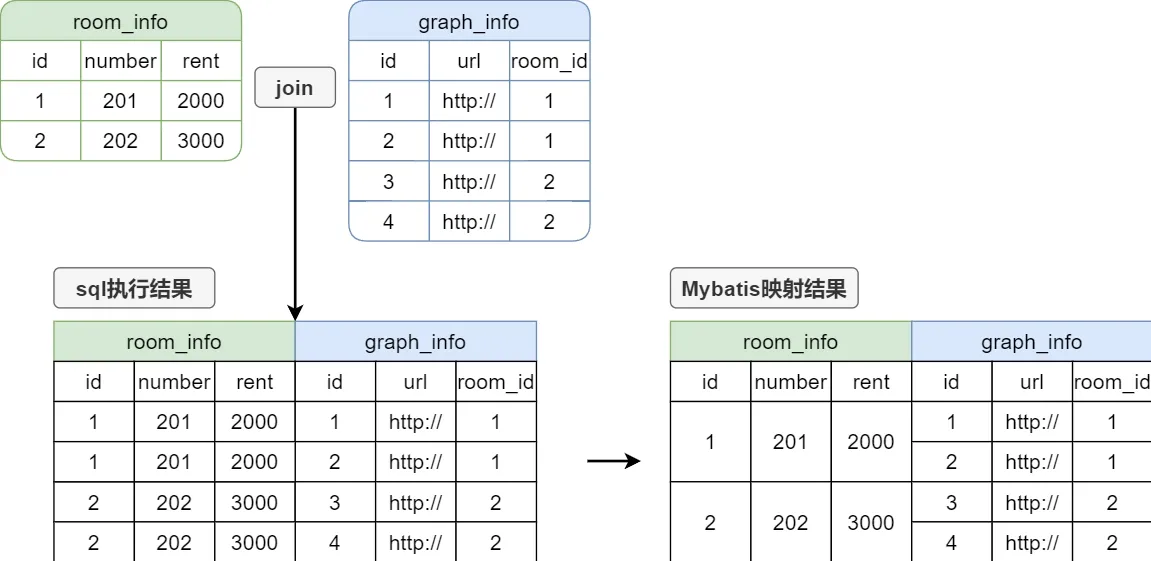
嵌套结果映射
<select id="selectRoomPage" resultMap="RoomPageMap"> select ri.id room_id, ri.number, ri.rent, gi.id graph_id, gi.url, gi.room_id from room_info ri left join graph_info gi on ri.id=gi.room_id </select> <resultMap id="RoomPageMap" type="RoomInfoVo" autoMapping="true"> <id column="room_id" property="id"/> <collection property="graphInfoList" ofType="GraphInfo" autoMapping="true"> <id column="graph_id" property="id"/> </collection> </resultMap>这种方式的执行原理如下图所示:
嵌套查询
<select id="selectRoomPage" resultMap="RoomPageMap"> select id, number, rent from room_info </select> <resultMap id="RoomPageMap" type="RoomInfoVo" autoMapping="true"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <collection property="graphInfoList" ofType="GraphInfo" select="selectGraphByRoomId" column="id"/> </resultMap> <select id="selectGraphByRoomId" resultType="GraphInfo"> select id, url, room_id from graph_info where room_id = #{id} </select>这种方法使用两个独立的查询语句来获取一对多关系的数据。首先,Mybatis会执行主查询来获取
room_info列表,然后对于每个room_info,Mybatis都会执行一次子查询来获取其对应的graph_info。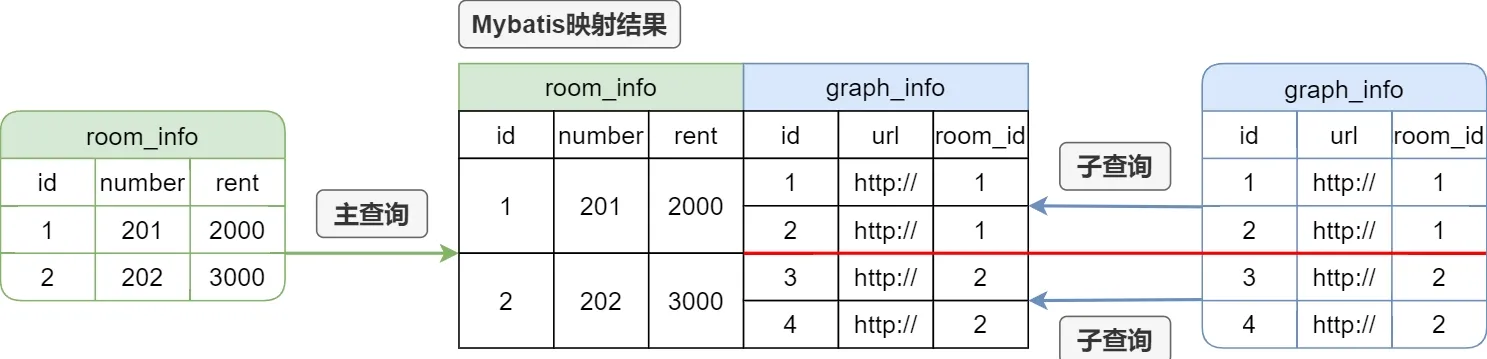
若现在使用MybatisPlus的分页插件进行分页查询,假如查询的内容是第1页,每页2条记录,则上述两种方式的查询结果分别是
嵌套结果映射

嵌套查询

显然嵌套结果映射的分页逻辑是存在问题的。
Redis缓存优化
1. 概述
缓存优化是一个性价比很高的优化手段,多数情况下,缓存优化可以通过一些简单的操作,换来性能的大幅提升。缓存优化的核心思想就是将一些原本保存在磁盘(例如MySQL)中的、经常访问并且查询开销比较大的数据,临时保存到内存(例如Redis)中。后序再访问相同数据时,就可直接从内存中获取结果,而无需再访问磁盘,由于内存的读写速度远高于磁盘,因此就能极大的提高程序的性能。

在使用缓存优化时,有一个问题不得不提,那就是数据库和缓存数据的一致性,当数据库中的数据发生变化时,缓存中的数据也要同步更新,否则就会出现数据不一致的问题,解决该问题的方案有如下几个
- 数据发生变化时,更新数据库的同时也更新缓存
- 数据发生变化时,更新数据库的同时删除缓存
进行缓存优化时,查询涉及多表访问,需要多次访问数据库的接口,查询代价较高,可以采取缓存优化,加快查询速度。
2. 自定义RedisTemplate
本项目使用Reids保存缓存数据,因此我们需要使用RedisTemplate进行读写操作。前文提到过,Spring-data-redis提供了StringRedisTemplate和RedisTemplate<Object,Object>两个实例,但是两个实例均不满足我们当前的需求,所以我们需要自定义RedisTemplate。
@Configuration
public class RedisConfiguration {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> stringObjectRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
template.setKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
template.setValueSerializer(RedisSerializer.java());
return template;
}
}3. 压力测试
使用Postman或者Apifox等工具对接口进行压力测试。

